Prospects for Bioethanol Production from Macroalgae
Abstract
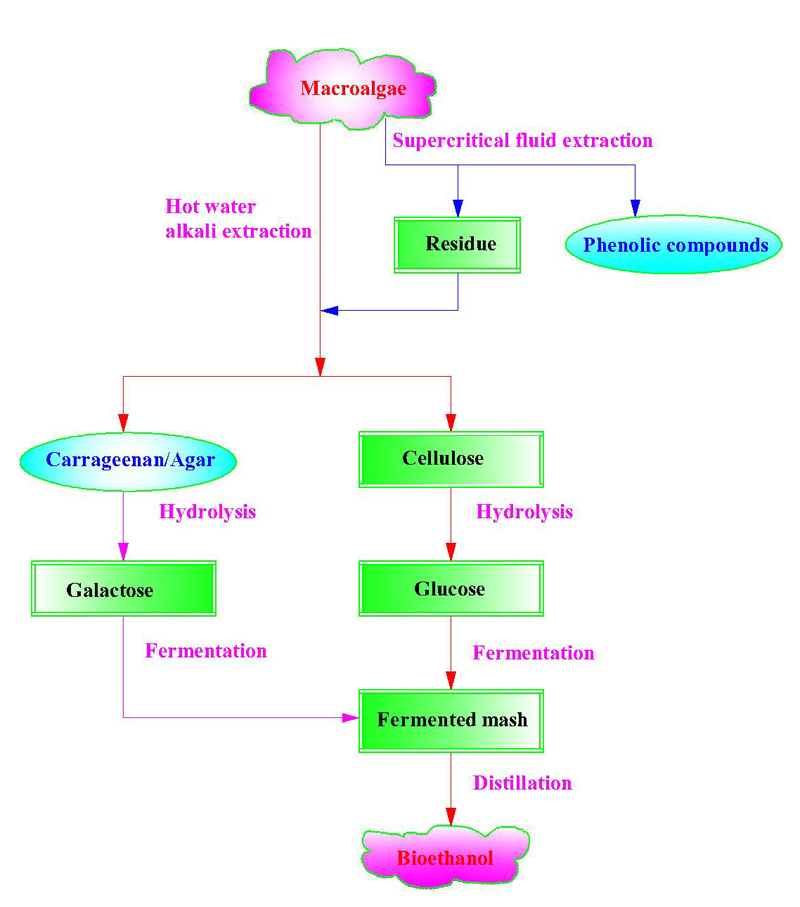
Macroalgae (mainly marine macroalgae, i.e. seaweeds) are considered as a very promising source for bioethanol production, because they have high carbohydrate contents, superior productivity, and wide adaptability. Macroalgae are generally grouped into three major categories: red, green, and brown algae. Each category has thousands of species, and each species possesses its unique cellular structure, biochemistry, and constitutes. Converting macroalgae to bioethanol involves pretreatment, saccharification, fermentation, and distillation; and the establishment of economic pretreatment methods is always the first key step for bioethanol production. In present, dilute-acid or alkali hydrolysis is typically used to treat macroalgal biomass. Macroalgae can be depolymerized under mild conditions as they have low lignin content. The resulting polysaccharides can be converted to ethanol through enzymatic hydrolysis, followed by adding bacteria, such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae and recombinant Escherichia coli KO11. Compared with the separate hydrolysis and fermentation process, the simultaneous saccharification and fermentation process often provided higher ethanol titer and conversion efficiency. However, the research on bioethanol production from macroalgae is still in its early stage due to both technical and economic barriers, significant amount of research and development work is needed prior to the commercialization of bioethanol manufacture from macroalgae.
Citation: Chen, J., Bai, J., Li, H., Chang, C., & Fang, S. (2015). Prospects for Bioethanol Production from Macroalgae. Trends in Renewable Energy, 1(3), 185-197. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.17737/tre.2015.1.3.0016
Keywords
Full Text:
FULL TEXT (PDF)References
Morales, M., Quintero, J., Conejeros, R., and Aroca, G. (2015). Life cycle assessment of lignocellulosic bioethanol: Environmental impacts and energy balance. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 42, 1349-1361. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.10.097
Bayrakci, A. G., and Koasar, G. (2014). Second-generation bioethanol production from water hyacinth and duckweed in Izmir: A case study. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 30, 306-316. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.10.011
Gupta, A., and Verma, J. P. (2015). Sustainable bio-ethanol production from agro-residues: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 41, 550-567. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.08.032
Goh, C. S., and Lee, K. T. (2010). A visionary and conceptual macroalgae-based third-generation bioethanol (TGB) biorefinery in Sabah, Malaysia as an underlay for renewable and sustainable development. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 14(2), 842-848. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2009.10.001
Chovau, S., Degrauwe, D., and Van der Bruggen, B. (2013). Critical analysis of techno-economic estimates for the production cost of lignocellulosic bio-ethanol. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 26, 307-321. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.05.064
Balat, M., Balat, H., and Oz, C. (2008). Progress in bioethanol processing. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 34(5), 551-573. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2007.11.001
Tan, I. S., and Lee, K. T. (2014). Enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation of seaweed solid wastes for bioethanol production: An optimization study. Energy, 78, 53-62. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.04.080
John, R. P., Anisha, G. S., Nampoothiri, K. M., and Pandey, A. (2011). Micro and macroalgal biomass: A renewable source for bioethanol. Bioresource Technology, 102(1), 186-193. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.139
Lawton, R. J., de Nys, R., and Paul, N. A. (2013). Selecting Reliable and Robust Freshwater Macroalgae for Biomass Applications. PLoS ONE, 8(5), e64168. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064168
Trivedi, N., Gupta, V., Reddy, C. R. K., and Jha, B. (2013). Enzymatic hydrolysis and production of bioethanol from common macrophytic green alga Ulva fasciata Delile. Bioresource Technology, 150, 106-112. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.09.103
Kumar, S., Gupta, R., Kumar, G., Sahoo, D., and Kuhad, R. C. (2013). Bioethanol production from Gracilaria verrucosa, a red alga, in a biorefinery approach. Bioresource Technology, 135, 150-156. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.10.120
Maceiras, R., Rodrı, M., Cancela, A., Urréjola, S., and Sánchez, A. (2011). Macroalgae: raw material for biodiesel production. Applied energy, 88(10), 3318-3323. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.11.027
Borines, M. G., de Leon, R. L., and McHenry, M. P. (2011). Bioethanol production from farming non-food macroalgae in Pacific island nations: Chemical constituents, bioethanol yields, and prospective species in the Philippines. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 15(9), 4432-4435. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2011.07.109
Chen, H., Zhou, D., Luo, G., Zhang, S., and Chen, J. (2015). Macroalgae for biofuels production: Progress and perspectives. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 47, 427-437. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.03.086
FAO (2012a). 2010 Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics. ftp://ftp.fao.org/FI/CDrom/CD_yearbook_2010/index.htm. (Accessed on 9/11/2015)
Roesijadi, G., Jones, S.B., Snowden-Swan, L. J., and Zhu, Y. (2010). Macroalgae as a Biomass Feedstock: A Preliminary Analysis. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory-19944.
Redmond, S., Green, L., Yarish, C., Kim, J., and Neefus, C. (2014). New England Seaweed Culture Handbook-Nursery Systems. http://seagrant.uconn.edu/publications/aquaculture/handbook.pdf. (Accessed on 9/11/2015)
Jung, K. A., Lim, S.-R., Kim, Y., and Park, J. M. (2013). Potentials of macroalgae as feedstocks for biorefinery. Bioresource Technology, 135, 182-190. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.10.025
Davis, T. A., Volesky, B., and Mucci, A. (2003). A review of the biochemistry of heavy metal biosorption by brown algae. Water Research, 37(18), 4311-4330. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00293-8
Wu, F.-C., Wu, J.-Y., Liao, Y.-J., Wang, M.-Y., and Shih, I.-L. (2014). Sequential acid and enzymatic hydrolysis in situ and bioethanol production from Gracilaria biomass. Bioresource Technology, 156, 123-131. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.024
Fasahati, P., Woo, H. C., and Liu, J. J. (2015). Industrial-scale bioethanol production from brown algae: Effects of pretreatment processes on plant economics. Applied Energy, 139, 175-187. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.11.032
Lobban, C. S., Wynne, M.J. ( 1981). The Biology of seaweeds. Blackwell Scientific Publications.
Kim, N.-J., Li, H., Jung, K., Chang, H. N., and Lee, P. C. (2011). Ethanol production from marine algal hydrolysates using Escherichia coli KO11. Bioresource Technology, 102(16), 7466-7469. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.04.071
Bucholc, K., Szymczak-Żyła, M., Lubecki, L., Zamojska, A., Hapter, P., Tjernström, E., and Kowalewska, G. (2014). Nutrient content in macrophyta collected from southern Baltic Sea beaches in relation to eutrophication and biogas production. Science of the Total Environment, 473, 298-307. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.044
Hou, X., Hansen, J. H., and Bjerre, A.-B. (2015). Integrated bioethanol and protein production from brown seaweed Laminaria digitata. Bioresource Technology, 197, 310-317. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.091
Wi, S. G., Kim, H. J., Mahadevan, S. A., Yang, D.-J., and Bae, H.-J. (2009). The potential value of the seaweed Ceylon moss (Gelidium amansii) as an alternative bioenergy resource. Bioresource Technology, 100(24), 6658-6660. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.07.017
Adams, J., Gallagher, J., and Donnison, I. (2009). Fermentation study on Saccharina latissima for bioethanol production considering variable pre-treatments. Journal of Applied Phycology, 21(5), 569-574. DOI: 10.1007/s10811-008-9384-7
Bharathiraja, B., Chakravarthy, M., Ranjith Kumar, R., Yogendran, D., Yuvaraj, D., Jayamuthunagai, J., Praveen Kumar, R., and Palani, S. (2015). Aquatic biomass (algae) as a future feed stock for bio-refineries: A review on cultivation, processing and products. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 47, 634-653. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.03.047
Lin, L.-h., Tako, M., and Hongo, F. (2000). Isolation and Characterization of I-Carrageenan from Eucheuma serra (Togekirinsai). Journal of Applied Glycoscience, 47(3-4), 303-310. DOI: 10.5458/jag.47.303
Khambhaty, Y., Mody, K., Gandhi, M. R., Thampy, S., Maiti, P., Brahmbhatt, H., Eswaran, K., and Ghosh, P. K. (2012). Kappaphycus alvarezii as a source of bioethanol. Bioresource Technology, 103(1), 180-185. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.10.015
Tan, I. S., and Lee, K. T. Comparison of different process strategies for bioethanol production from Eucheuma cottonii: An economic study. Bioresource Technology. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.008
Meinita, M. D. N., Hong, Y.-K., and Jeong, G.-T. (2012). Detoxification of acidic catalyzed hydrolysate of Kappaphycus alvarezii (cottonii). Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 35(1-2), 93-98.
Park, J.-H., Hong, J.-Y., Jang, H. C., Oh, S. G., Kim, S.-H., Yoon, J.-J., and Kim, Y. J. (2012). Use of Gelidium amansii as a promising resource for bioethanol: A practical approach for continuous dilute-acid hydrolysis and fermentation. Bioresource Technology, 108, 83-88. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.12.065
Kim, H. M., Wi, S. G., Jung, S., Song, Y., and Bae, H.-J. (2015). Efficient approach for bioethanol production from red seaweed Gelidium amansii. Bioresource Technology, 175, 128-134. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.050
Wang, X., Liu, X., and Wang, G. (2011). Two-stage Hydrolysis of Invasive Algal Feedstock for Ethanol FermentationF. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 53(3), 246-252. DOI: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2010.01024.x
Lee, H. Y., Jung, K. H., and Yeon, J. H. (2011). Repeated-batch operation of surface-aerated fermentor for bioethanol production from the hydrolysate of seaweed Sargassum sagamianum. Journal of microbiology and biotechnology, 21(3), 323-331.
Wargacki, A. J., Leonard, E., Win, M. N., Regitsky, D. D., Santos, C. N. S., Kim, P. B., Cooper, S. R., Raisner, R. M., Herman, A., and Sivitz, A. B. (2012). An engineered microbial platform for direct biofuel production from brown macroalgae. Science, 335(6066), 308-313.
Jang, J.-S., Cho, Y., Jeong, G.-T., and Kim, S.-K. (2012). Optimization of saccharification and ethanol production by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (SSF) from seaweed, Saccharina japonica. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 35(1-2), 11-18. DOI: 10.1007/s00449-011-0611-2
Trivedi, N., Reddy, C. R. K., Radulovich, R., and Jha, B. (2015). Solid state fermentation (SSF)-derived cellulase for saccharification of the green seaweed Ulva for bioethanol production. Algal Research, 9, 48-54. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2015.02.025
Pilavtepe, M., Sargin, S., Celiktas, M. S., and Yesil-Celiktas, O. (2012). An integrated process for conversion of Zostera marina residues to bioethanol. The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 68, 117-122. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2012.04.019
Jol, C. N., Neiss, T. G., Penninkhof, B., Rudolph, B., and De Ruiter, G. A. (1999). A Novel High-Performance Anion-Exchange Chromatographic Method for the Analysis of Carrageenans and Agars Containing 3,6-Anhydrogalactose. Analytical Biochemistry, 268(2), 213-222. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/abio.1998.3059
Kim, C., Ryu, H. J., Kim, S. H., Yoon, J.-J., Kim, H. S., and Kim, Y. J. (2010). Acidity tunable ionic liquids as catalysts for conversion of agar into mixed sugars. Bull Korean Chem Soc, 31(2), 511-514.
Quemener, B., and Lahaye, M. (1998). Comparative analysis of sulfated galactans from red algae by reductive hydrolysis and mild methanolysis coupled to two different HPLC techniques. Journal of Applied Phycology, 10(1), 75-81.
Zhang, B., Wang, L., Shahbazi, A., Diallo, O., and Whitmore, A. (2011). Dilute-sulfuric acid pretreatment of cattails for cellulose conversion. Bioresource Technology, 102(19), 9308-9312. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.07.008
Azevedo, G., Hilliou, L., Bernardo, G., Sousa-Pinto, I., Adams, R. W., Nilsson, M., and Villanueva, R. D. (2013). Tailoring kappa/iota-hybrid carrageenan from Mastocarpus stellatus with desired gel quality through pre-extraction alkali treatment. Food Hydrocolloids, 31(1), 94-102. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.10.010
Uju, Wijayanta, A. T., Goto, M., and Kamiya, N. (2015). Great potency of seaweed waste biomass from the carrageenan industry for bioethanol production by peracetic acid-ionic liquid pretreatment. Biomass and Bioenergy, 81, 63-69. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2015.05.023
Ortiz, J., Romero, N., Robert, P., Araya, J., Lopez-Hernández, J., Bozzo, C., Navarrete, E., Osorio, A., and Rios, A. (2006). Dietary fiber, amino acid, fatty acid and tocopherol contents of the edible seaweeds Ulva lactuca and Durvillaea antarctica. Food Chemistry, 99(1), 98-104. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.07.027
Kirchmajer, D. M., Steinhoff, B., Warren, H., Clark, R., and in het Panhuis, M. (2014). Enhanced gelation properties of purified gellan gum. Carbohydrate Research, 388, 125-129. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2014.02.018
Li, Y., Huang, Z., Qiao, L., Gao, Y., Guan, H., Hwang, H., Aker, W. G., and Wang, P. (2015). Purification and characterization of a novel enzyme produced by Catenovulum sp. LP and its application in the pre-treatment to Ulva prolifera for bio-ethanol production. Process Biochemistry, 50(5), 799-806. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2015.02.013
Schultz-Jensen, N., Thygesen, A., Leipold, F., Thomsen, S. T., Roslander, C., Lilholt, H., and Bjerre, A. B. (2013). Pretreatment of the macroalgae Chaetomorpha linum for the production of bioethanol-Comparison of five pretreatment technologies. Bioresource Technology, 140, 36-42.
Borines, M. G., de Leon, R. L., and Cuello, J. L. (2013). Bioethanol production from the macroalgae Sargassum spp. Bioresource Technology, 138, 22-29. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.03.108
Roesijadi, G., Copping, AE, Huesemann, MH, Forster, J, Benemann, JR. (2008). Technoeconomic feasibility analysis of offshore seaweed farming for bioenergy and biobased products. Battelle Pacific Northwest Division Report.
Rezania, S., Ponraj, M., Din, M. F. M., Songip, A. R., Sairan, F. M., and Chelliapan, S. (2015). The diverse applications of water hyacinth with main focus on sustainable energy and production for new era: An overview. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 41, 943-954. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.09.006
Aitken, D., Bulboa, C., Godoy-Faundez, A., Turrion-Gomez, J. L., and Antizar-Ladislao, B. (2014). Life cycle assessment of macroalgae cultivation and processing for biofuel production. Journal of Cleaner Production, 75, 45-56. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.03.080
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.17737/tre.2015.1.3.0016
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2015 Junying Chen, etc.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.Copyright @2014-2025 Trends in Renewable Energy (ISSN: 2376-2136, online ISSN: 2376-2144)
